Aligning rasters for analysis
I’ve been working on tooling the past few days, mostly gathering in one place scripts I’ve written for other projects.
A key part of my workflow is loading multiple rasters into spatially-aligned arrays of the same shape for analysis. This lets me compare the interpolated values over the same area of interest to get a sense of the dataset quality
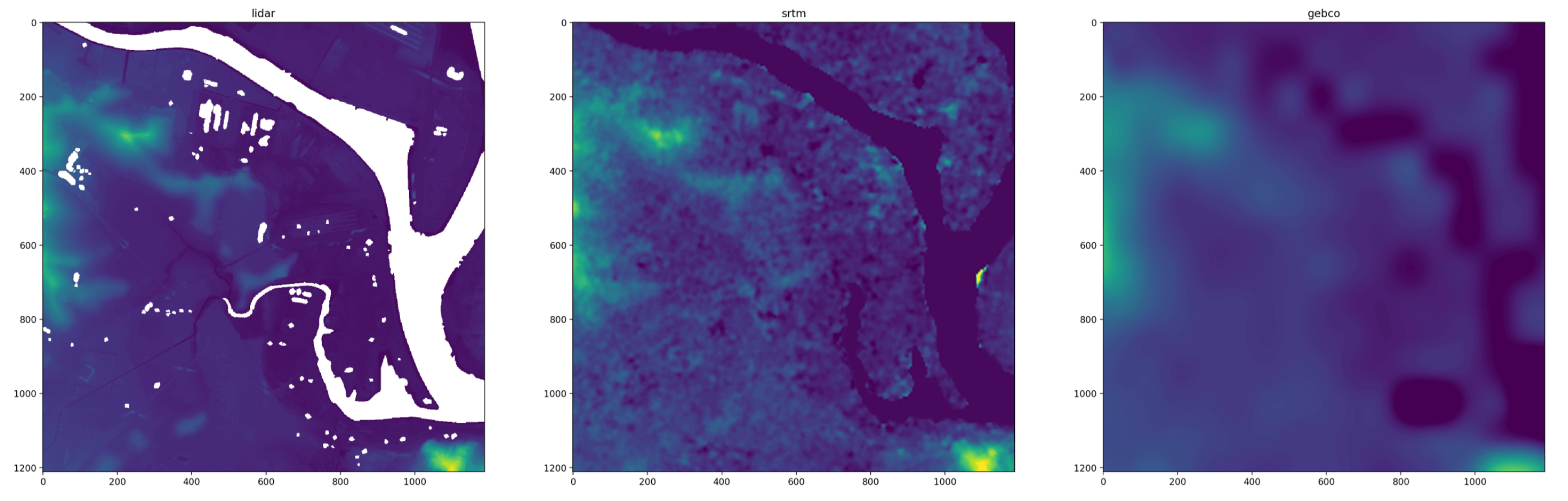
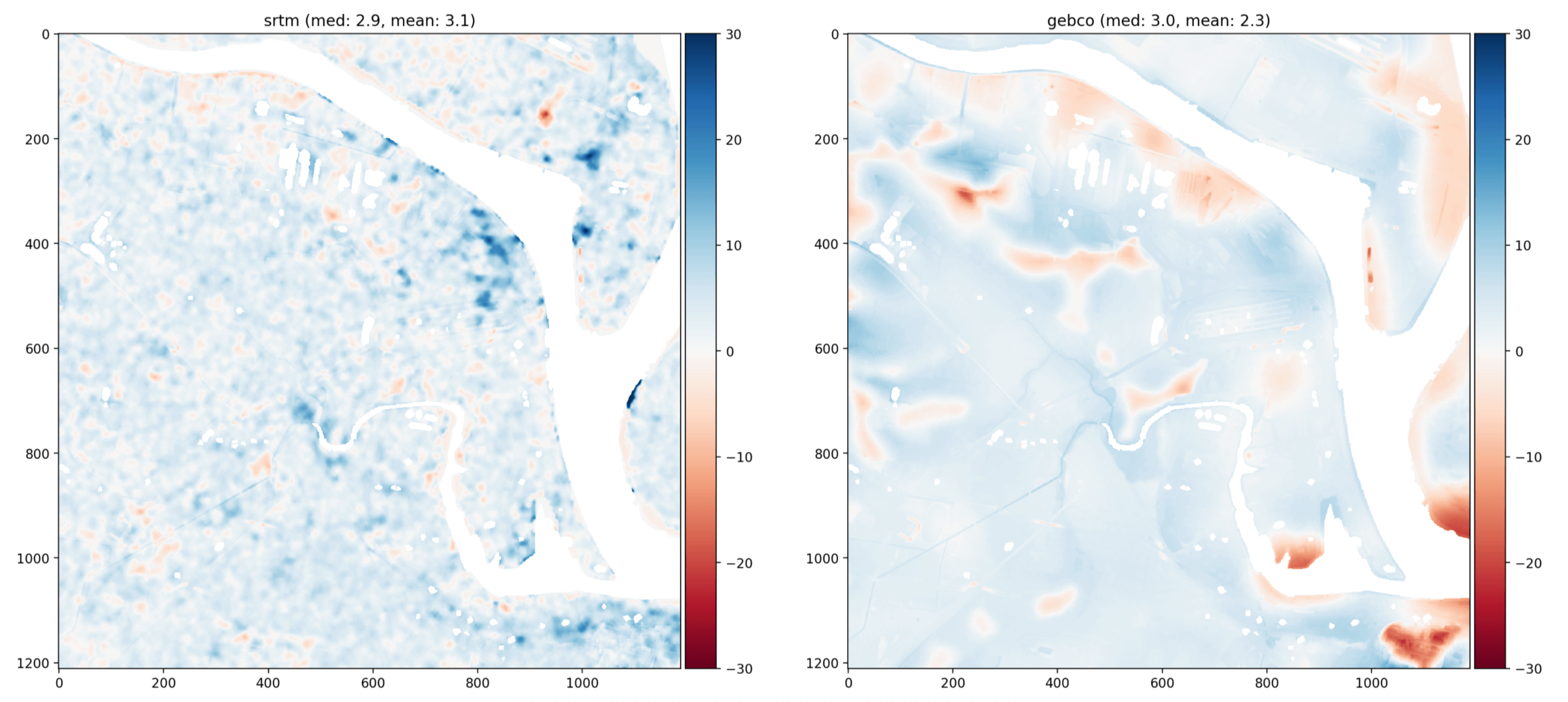
and because the arrays are the same shape it’s easy to do vectorised analysis, like the difference against a hi-res lidar DEM
Here’s the code I use:
import math
import os
import random
import string
import subprocess
import sys
import tempfile
import geopy.distance
import matplotlib
import numpy as np
import pyproj
import rasterio
WGS84_LATLON_EPSG = 4326
TMP_FOLDER = '/tmp/raster-utils/'
def run_cmd(cmd):
'''Run a command.
Raises ValueError if nonzero exit code.
'''
r = subprocess.run(cmd, shell=shell, capture_output=True)
assert r.returncode == 0
def random_string(n=16):
return ''.join(random.choices(string.ascii_lowercase, k=n))
def tmp_file_path(extension='', filename=None):
'''Random temporary file.'''
os.makedirs(TMP_FOLDER, exist_ok=True)
filename = filename or random_string(16) + extension
path = os.path.join(tmp_folder, filename)
return path
def offset_lat_lon(lat, lon, dist, bearing_degrees):
'''
Shift a latlon point by a Cartesian vector.
From github.com/kellydunn/golang-geo/blob/master/point.go
'''
dist_ratio = dist / radius_of_earth(lat)
bearing = math.radians(bearing_degrees)
lat_1 = math.radians(lat)
lon_1 = math.radians(lon)
lat_2_part_1 = math.sin(lat_1) * math.cos(dist_ratio)
lat_2_part_2 = math.cos(lat_1) * math.sin(dist_ratio) * math.cos(bearing)
lat_2 = math.asin(lat_2_part_1 + lat_2_part_2)
lon_2_part_1 = math.sin(bearing) * math.sin(dist_ratio) * math.cos(lat_1)
lon_2_part_2 = math.cos(dist_ratio) - (math.sin(lat_1) * math.sin(lat_2))
lon_2 = lon_1 + math.atan2(lon_2_part_1, lon_2_part_2)
lat_2 = math.degrees(lat_2)
lon_2 = math.degrees(lon_2)
return lat_2, lon_2
def radius_of_earth(lat):
'''
Find the radius of the Earth at a given latitude. Vectorised.
Formula and data from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Earth_radius
'''
r_1 = 6378137.0 # Earth equatorial radius
r_2 = 6356752.3 # Earth polar radius
lat = np.radians(lat)
part_1 = r_1**4 * np.cos(lat)**2 + r_2**4 * np.sin(lat)**2
part_2 = r_1**2 * np.cos(lat)**2 + r_2**2 * np.sin(lat)**2
return np.sqrt(part_1 / part_2)
def load_aligned_raster(path, epsg=None, bounds=None, shape=None, bounds_epsg=None, align_to=None):
'''Load raster from file.
epsg(int): reproject raster.
bounds: in final cps (epsg if provided else file)
shape: control resolution (for aligning grids, will interpolate)
bounds_epsg: if bounds aren't in new epsg.
align_to: rasterio file handle, to take parameters from.
Returns both numpy array and rasterio file handle.
'''
# Auto aligned to another file.
if align_to is not None:
return load_aligned_raster(
path,
epsg=align_to.crs.to_epsg(),
bounds=align_to.bounds,
shape=align_to.shape,
)
# Normalise inputs.
if isinstance(epsg, str):
epsg = epsg.lower().replace('epsg:', '')
epsg = int(epsg)
if bounds is not None:
bounds = np.asarray(bounds)
if isinstance(shape, int):
shape = shape, shape
# Get raster metadata.
with rasterio.open(path) as f:
f_res = f.res
f_epsg = f.crs.to_epsg()
f_bounds = np.array(f.bounds)
f_shape = f.shape
# Check if any transforms are needed.
transform_needed = False
if epsg and epsg != f_epsg:
transform_needed = True
if (bounds is not None) and not np.allclose(bounds, f_bounds):
transform_needed = True
if shape and shape != f_shape:
transform_needed = True
# Do transform.
if transform_needed:
transformed_path = tmp_file_path('.tiff')
cmd = [
'gdalwarp',
'-novshiftgrid',
'-r', 'bilinear',
'-multi',
'-ot', 'Float32',
'-q',
'-wo', 'NUM_THREADS=val/ALL_CPUS',
'-co', 'NUM_THREADS=ALL_CPUS',
'-co', 'ZLEVEL=1',
'-co', 'COMPRESS=DEFLATE',
'-co', 'PREDICTOR=1',
'-co', 'BIGTIFF=YES',
'-co', 'TILED=YES',
]
if epsg:
cmd += ['-t_srs', f'EPSG:{epsg}']
if shape:
cmd += ['-ts', str(shape[1]), str(shape[0])]
if bounds is not None:
cmd += ['-te'] + [str(x) for x in bounds]
if bounds is not None and bounds_epsg:
cmd += ['-te_srs', f'EPSG:{bounds_epsg}']
cmd += [path, transformed_path]
run_cmd(cmd)
else:
transformed_path = path
# Load.
with rasterio.open(transformed_path) as f:
a = f.read(1, masked=True, out_dtype=float)
a = np.ma.filled(a, np.nan)
# Validate.
if shape:
assert shape == f.shape
return a, f
def radius_bounds(centre_lat, centre_lon, size_m):
radius_m = np.sqrt(size_m**2 * 2)
top, right = offset_lat_lon(centre_lat, centre_lon, dist=radius_m, bearing_degrees=45)
bottom, left = offset_lat_lon(centre_lat, centre_lon, dist=radius_m, bearing_degrees=180+45)
bounds = rasterio.coords.BoundingBox(left, bottom, right, top)
return bounds
Datasets can then be loaded like this:
# Make bounds.
centre_lat = -32.903
centre_lon = 151.752
size_m = 30*100
bounds = radius_bounds(centre_lat, centre_lon, size_m)
# Paths.
lidar_path = '~/gpxz-dataset/data/audem.vrt'
srtm_path = '~/gpxz-dataset/data/srtm30m.vrt'
gebco_path = '~/gpxz-dataset/data/gebc2020.vrt'
# Load rasters.
a_lidar, f_lidar = load_aligned_raster(lidar_path, bounds=bounds, bounds_epsg=WGS84_LATLON_EPSG)
a_srtm, f_srtm = load_aligned_raster(srtm_path, align_to=f_lidar)
a_gebco, f_gebco = load_aligned_raster(gebco_path, align_to=f_lidar)